The plants get their water from the soil, and the earth receives it naturally from rain. It is a well-known fact that crops need extra water when there is no rain. In such cases, watering the yield from a particular water source is called Irrigation.
The three primary soil moisture levels are saturation, field capacity, and permanent wilting point. The optimum soil water quality for a plant is the “field capacity,” the minimum water quality is the amount of soil water in the “permanent wilting point.” Here the roots have the optimal volume of water, and the root hairs receive the air they need for respiration through the soil pores.
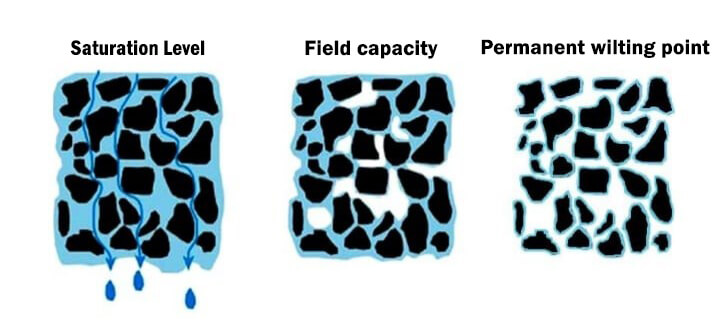
The plant root system finds it difficult to absorb water as soil water leaves the atmosphere through the soil in various ways. In irrigation, it is important to bring the soil water level to the water level of the field capacity by applying water before the soil dries out, that is, before it reaches the “permanent wilting coefficient”.
In this way, proper water supply for coconut cultivation helps to increase the yield of coconut and the healthy growth of the coconut tree. Irrigation with moisture conservation methods is very practical in managing coconut cultivation. An adult coconut tree needs 50 liters of water per day and a coconut plant needs between 10 or 15 liters of water per day.
- Clay pot irrigation
This method is suitable for coconut seedlings during the dry season in the dry and intermediate zone. But this method is not practical for watering the mature coconut trees. What happens here is that the water in the pot slowly leaks through its walls (the unpainted part) to the outside through osmotic pressure. The porous nature of the clay walls helps the soil to absorb water through the clay wall.
This irrigation system can be introduced to the field following a few steps.
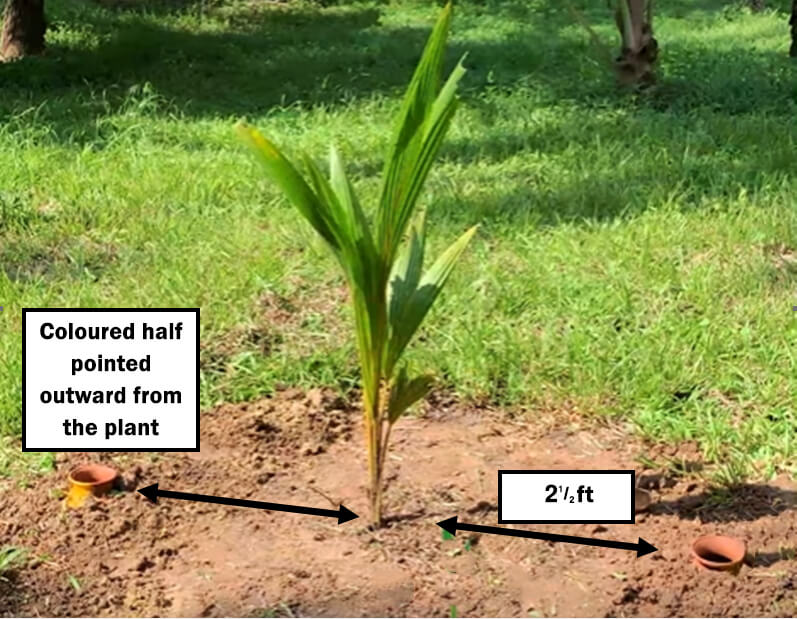
- Provide two clay pots each with a capacity of 15-20 liters and coat each half with a liquid like lacquer.
- Bury the pots with the mouth open about 2 inches above the ground and 2 feet from the coconut plant.
- Position the two pots as shown below in the direction of the pot lacquer, away from the plant.
- Fill with water, usually once a week, and cover each mouth tightly. This is to prevent sludge from settling in the mud and sand with running water during the rainy season. (In dry season, water twice a week)
- Eventually through the unpainted half of each pot, water leaks into the soil around the plant.

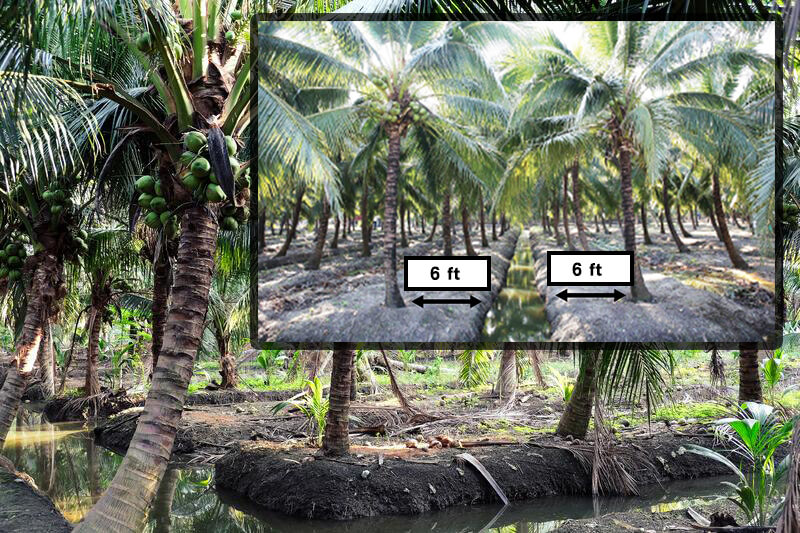
- Canal irrigation
Canal irrigation is a successful method used by many coconut growing countries such as Malaysia and Thailand. In this method the water requirement is supplied directly and the nuts can be safely plucked into the canals during harvesting period.
- Apply 6/8 feet from the base of the coconut tree to each row of trees and about 1/3 foot of the canal.
- Coconut seedlings should be planted in the correct manner or in a rectangular pattern with a minimum spacing of 24 feet.
- There must be a suitable water source to supply water to the canal and this is more practical for flat ground.
- This is not suitable for sandy soils as water seeps into the soil very quickly.#

- Horse irrigation system
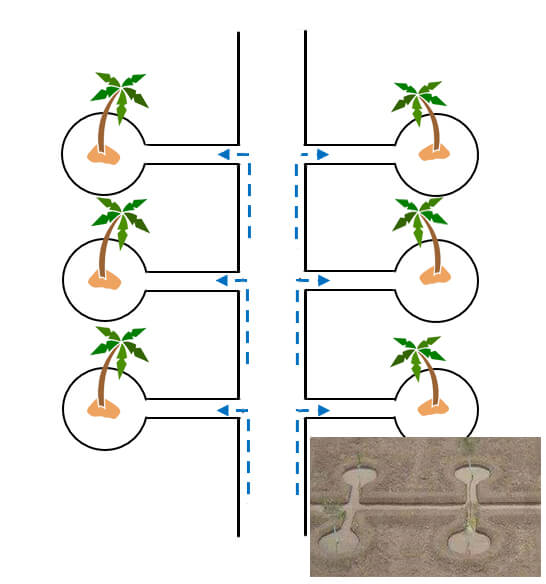
A practical irrigation system that can be used for coconut cultivation in Sri Lanka. The water is supplied to the coconut tree through hoses connected to the PVC pipe system installed in the land. Since the main PVC pipe system is buried under the ground, weeding and picking of coconuts can be done without any hindrance.
When burying the pipes, the total area of the cultivated land should be measured and if the seedlings are planted with a square spacing, the pipes can be planned properly before burying. The PVC main pipe is installed in the ground, leaving a gap between the rows to double the length of the hose, and the hose pipe units are connected to the main PVC pipe system.
To supply water to the piping system, an elevated water source (lift) or a pressure water source must be used. Rubber hoses are primarily used for hose units and their lengths should be chosen to suit their cultivation. It can also be used to irrigate intercrops without making major changes to the system.

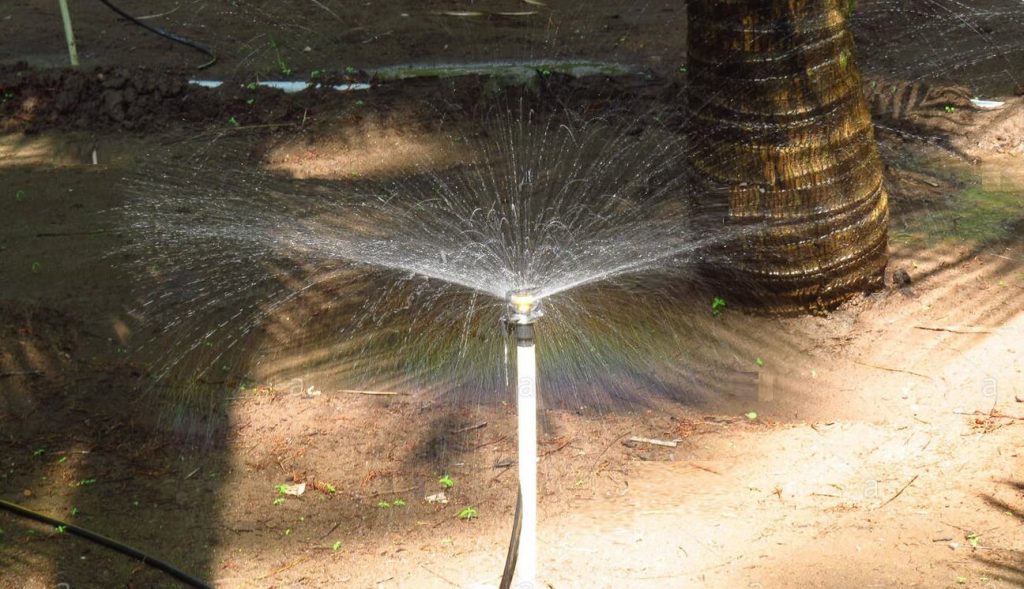
- Sprinkler irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation supplies water to the entire area around the tree and covers about 10 feet in diameter around the tree. In this method, which is most suitable for coconut nurseries, the discharge pipe is connected to a water source higher than the cultivation area. Water should reach the dispersing units at an average pressure of 200 – 340 kPa.
There are no separate water supply units for coconut trees. Water wastage is high as water is applied to the entire soil around the coconut trees. But the system is very helpful in absorbing the fertilizer to the roots. This irrigation system creates a microclimate conducive to the growth of soil organisms such as earthworms and aids in the release of organic nutrient tree roots through natural digestive processes. Sprinkler irrigation also benefits from labor saving, importance for intercropping, ease of operation, and durability.

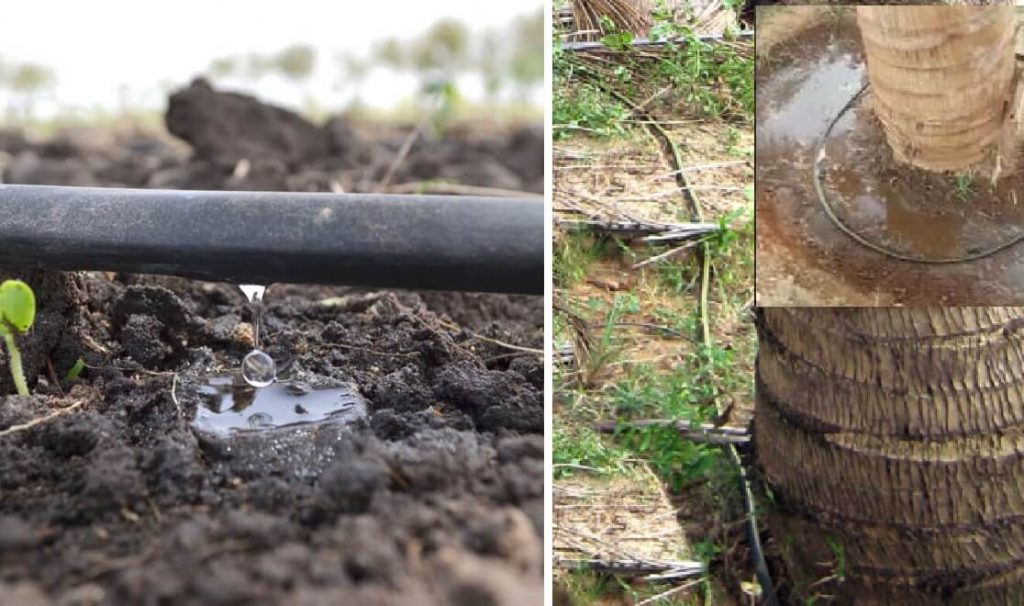
- Drip Irrigation
This drip irrigation system has been introduced to minimize water wastage during irrigation. These drippers can be applied to several or more places in the manure circle of the tree. In comparison, this is the most suitable irrigation system for coconut cultivation. It does not require as much pressure as the sprinkler system. Here too, the water should reach the micro water sprinkling units at a pressure of 170–205 kPa through a water source (lift) higher than the cultivated area.
About ¾ inches of PVC pipe is connected to the main water supply, and each of the main pipes is laid between rows of trees (as in the middle of two rows of trees). The drippers are installed in tubes so that they reach the manure circle of each tree or tree. Usually three or four drippers are applied to a tree.
Advantages of drip irrigation
- Ability to supply the required amount of water only to the extent of the roots of the coconut tree.
- Coconut trees can be adequately watered with a minimum amount of water Minimizing water wastage.
- Ability to supply fertilizer to the coconut tree through the water system itself.
- It can also irrigate by-products through simple modifications.
- Energy and labor saving.
- Reduces weed growth.

- Basin Irrigation
Basins of about 10 cm depth are formed around the coconut tree to cover the root zone of the coconut tree. These basins are connected by small drains, which supply water to each coconut tree. This method is not suitable for flat or irregularly sloping lands as well as sandy soils. It is also difficult to supply the coconut tree with the amount of water determined by this method.
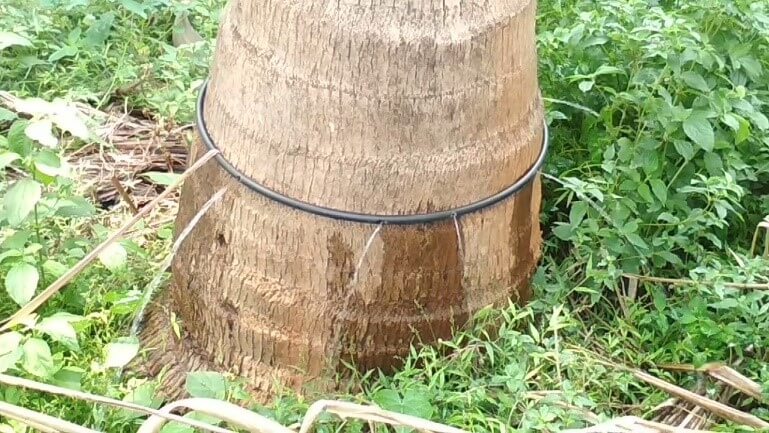
- Griddle Water Supply
The installation of the piping system and other accessories is often similar to a drip irrigation system. This irrigation system differs from the drip irrigation system in that the drippers are located around the base of the coconut tree as shown below. Here water is supplied around the trunk of the coconut tree.

2022.01.04


Leave a Reply